hardness test hrc meaning|rockwell hrc scale chart : exporters Rockwell hardness testing is a useful and efficient way to determine the hardness of a material. It measures the depth of penetration of an indenter on the material being tested, making it possible to calculate its relative hardness and .
Resultado da Telegram: Contact @novidadesfatalmodel Novidades Fatal Model. Quer ficar por dentro do que acontece no Fatal Model? Participe de pesquisas, enquetes e receba .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webksg_aoty. ADMIN MOD. 'Top Gun: Maverick' Review Thread. Review. Rotten Tomatoes: TBD. Metacritic: 81/100 (37 critics) As with other movies, the scores are set to change as .
The most common is the static load indentation hardness test, such as Brinell Hardness (HB), Rockwell Hardness (HRA, HRB, HRC), and Vickers Hardness (HV). These hardness values indicate the ability of a .
Different hardness scales employ their own combinations of test forces and test indentations (cone, ball etc.) and are adapted to the type of material being tested. In the cutlery industry, the most often used scale is the Rockwell scale (HRC). HRC: Diamond cone, 150 kg load, for harder materials. The hardness value is determined by the depth of the indentation. Vickers Hardness (HV): Suitable for microscopic analysis. Uses a diamond square cone indenter . These are a numeric number representing hardness, two letters “HR”, abbreviations representing “Rockwell hardness”, and the Rockwell scale designation, which shows the load .Indentation hardness value is obtained by measuring the depth or the area of the indentation using one of over 12 different test methods. Learn more about hardness testing basics here. The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined .
Rockwell hardness testing is a useful and efficient way to determine the hardness of a material. It measures the depth of penetration of an indenter on the material being tested, making it possible to calculate its relative hardness and . One common grade is C, HRC, which uses a 150kgf total load and a 120° diamond cone indenter that is loaded twice. First, an initial load of P1=10kgf is applied to ensure proper contact between the indenter and the .Hardness measures the resistance to localized plastic deformation caused by force or abrasion. Materials with high hardness would generally be stronger and more wear-resistant but, on the other hand, more brittle and sensitive to .
rockwell steel hardness chart
Rockwell C to Brinell Hardness Conversion Chart. While the Rockwell hardness testing scale is prevalent, it is best to consider the material thickness and softness to select the most suitable .Before application of the Rockwell hardness test, you must prepare the surface of the material to be tested. The required surface condition for the Rockwell hardness test depends on the load used. The Rockwell hardness test is . Rockwell hardness definition: 0.002mm residual indentation depth is a Rockwell hardness unit. K – constant, 130 for steel ball indenter and 100 for diamond indenter . Hardness test characteristics. ① The stress state .For example, “HRC 96” for a metal means the hardness of that metal is 96 when measured using Rockwell hardness scale C. Manufactured products are made of different types of materials. To accommodate the hardness testing of this .
Rockwell Hardness HRC Scale Definition . Reference values for HRC Symbol Test parameter Reference value Start measurement Stop measurement . F. 0. Preliminary . test force. 98,066 5 N. 1 -F . Total test force. 1 470,997 5 -N. 1-α. Included angle of the indenter cone (between surface axial-plane line segments) 120⁰
Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via a diamond in this method. ⑵Rockwell hardness (HR) When HB>450 or the sample is too small, the Brinell hardness test cannot be used and the Rockwell hardness measurement can be used instead. It uses a diamond cone with an apex angle of 120° or a steel ball with a diameter of 1.59 and 3.18mm, which is pressed into the surface of the material to be tested under a .Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). The Rockwell scale was cocreated by Hugh and Stanley Rockwell in the early 20th century to test the hardness of different materials. There are several different scales by which a material’s hardness is measured on, but blade steels are measured on the C scale. (HRC means Hardness on Rockwell scale C.)
There are many methods of hardness test, the principle is different, and the measured hardness value and meaning are also different. The most commonly used is the static load indentation hardness test, that is, Brinell hardness HB, Rockwell hardness HRA, HRB, HRC, Vickers hardness HV, rubber and plastic Shore hardness HA, HD, and other hardness . Regardless of its intended use, any good knife should have a hardness rating between 52 HRC and 64 HRC. Super-hard knives are great for kitchen duties where accurate, thin slices must be made regularly. Softer knives are better for chopping and heavy-duty work, where resistance to breaking and chipping are more important than sharpness. . What is hardness, then? To provide a somewhat circular and not very helpful definition, it's a measure of how a material performs in a hardness test. This brings us to the subject of hardness testing. One of the hardness tests most commonly used in the US was developed by Hugh Rockwell and Stanley Rockwell in 1914.
Rockwell C HRC (120 degree cone 150 kg) Rockwell B HRB (1/16" ball 100 kg) Leeb HLD [1] 800-72-856 780: 1220: 71-850 760: 1210: 70-843 745: 1114: 68-837 725: . "Standard Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell Hardness, Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, Scleroscope Hardness .In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by pressing or abrasion.In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as .The Rockwell test is particularly suitable for measuring the hardness of hardened metals and alloys. These materials often have high hardness levels and require higher applied loads to create an indentation. The Rockwell C scale (HRC) is commonly used for harder materials. Hardened Materials The Rockwell hardness test is less affected by .
Proposed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering and metallurgy.The large size of indentation and possible damage to test-piece limits its . HV, HB, HRC Hardness Comparison Chart. Hardness testing is the simplest and most straightforward method among mechanical property tests. In order to replace certain mechanical property tests with hardness tests, a .A Vickers hardness tester. The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. [1] The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter .
Related reading: Metal Hardness Comparison Chart: HV, HB, HRC Commonly Used Hardness Brinell Hardness. The Brinell hardness test uses a ball made of hardened steel or a hard alloy with a diameter of D as the indenter.. A specified test force F is applied to the surface of the material being tested, and after a designated hold time, the test force is . In the Rockwell Hardness test, The indenter – a diamond cone with a rounded tip or a steel sphere – is pressed into the test piece in two stages. . Low penetration depths mean high levels of hardening, while high penetration depths are characteristic of soft materials. . The Unit of Rockwell hardness is HRC. The indentor in Rockwell .Brinell [HB] is one of the most common units used for listing the hardness of steel materials. The test is done with a 10 mm steel ball pressed with 3000 Kgf (6,614 Lbf). Common values for machined materials range from 100 HB for very soft materials up to 650 HB for heat-treated steels.. The advantage of Brinell [HB] over Rockwell [HRC/HRB], is that the whole range is .
profiles. The Rockwell test is the most popular indentation hardness test and is used in a wide variety of applications. Advantages of the Rockwell Test There are several reasons for the popularity of the Rockwell test. The test itself is very rapid. On a manually operated unit, a Rockwell test takes only five to ten seconds,
Brinell and Rockwell Hardness Conversion Chart - These Conversion Tables presents data in the Rockwell A, B, C, D, E and F hardness range on the relationship among .Brinell Hardness HB: Rockwell C - HRC: Rockwell B - HRB: Vickers - HV : Enter a figure into any of the fields and click calculate, the nearest values in each scale is shown, or zero if out of range. Values are approximate and for guidance only. Reference Table: Steel hardness conversion chart - all values approximate. After the preliminary test force has been applied for a short time, the dial gauge is set to zero (reference level). The actual hardness value can then be determined. Figure: Rockwell hardness test procedure. The actual test load F 1 is applied in addition to the preload and the indetor penetrates the material with the total force F=F 0 +F1 .The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can be also used as a microhardness test method, which is mostly used for small parts, thin sections, or case depth work. Since the .
What is Hardness – Definition. In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation (localized plastic deformation) and scratching. . HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale. . The Knoop hardness test method is one of microhardness tests – tests for mechanical hardness used .So what does this mean? You can’t use the Rockwell method for testing the hardness of .020″ shim stock if it’s supposed to be 60 HRC. Just be aware that there are minimum thicknesses in the 0.040″ and under range so you can look up the reference if you should ever need to. Brinell Hardness Test
rockwell scale vs hrc
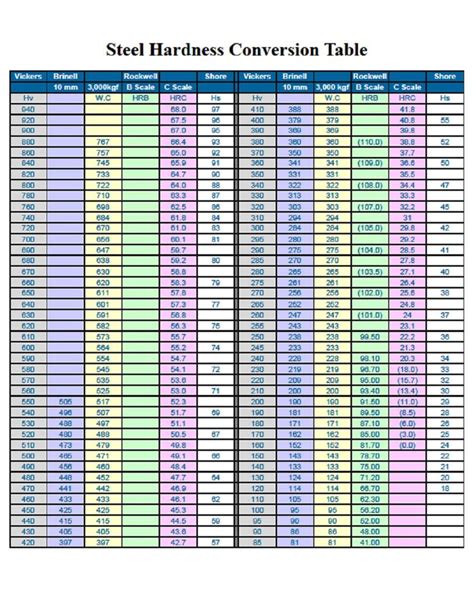
rockwell hrc scale chart
karl fischer volumetric titrator for moisture determination commercial
WEBWeTransfer is the simplest way to send your files around the world. Share large files and photos. Transfer up to 2GB free. File sharing made easy!
hardness test hrc meaning|rockwell hrc scale chart